'MCU 및 PLD'에 해당되는 글 11건
- 2012.08.09 perpetual bootloader mode 에 대하여..
- 2012.01.02 avrstudio 컴파일 에러.. 8
- 2011.11.30 시중에 굴러다니는 싸구려 avrusbisp 에 대하여.. 1
- 2010.08.02 아두이노 - 내장 라이브러리 사용 스테핑 모터 구동 소스.
- 2010.08.02 아두이노 - 스테핑 모터 컨트롤러(SLA7062M) 소스
- 2010.07.16 아두이노 wmp 소스
- 2009.10.14 atiny2313 - 테스트 소스.
- 2008.09.21 max7000시리즈에서 jtag 핀을 IO 핀으로 쓸 수 있을까요? - yes...(2)
- 2008.09.21 FPGA 디바이스 CONFIGURATION
- 2008.09.21 MAX3000과 MAX7000 시리즈의 차이점.
perpetual bootloader mode 에 대하여..
In this mode, Maple stays a DFU device and does not jump to user code until the next reset. This is useful for guaranteeing that your Maple will be available for reprogramming.
To put your Maple (or other Maple board) into perpetual bootloader mode:
- Plug your board into the USB port.
- Hit the reset button (it’s the button labeled RESET). Notice that your board blinks quickly 6 times, then blinks slowly a few more times.
- Hit reset again, and this time push and hold the other button during the 6 fast blinks (the normal button is labeled BUT). You can release it once the slow blinks start.
그러나 이렇게 한 후에도 여전히 문제점은 남아있다.
메이플 보드에는 PA4 핀이 BOOT0 핀과 묶여있다.
따라서 PA4 핀도 BUT 버튼이 눌릴 때에 같이 0 으로 떨어진다.
망고보드에서 BOOT0 핀은 외부 핀으로 빠져있지 않기 때문에, 안타깝게도 보드에 인두를 대야 하는 상황이 발생한다.
현재 이런 개조를 할것인지 고려중이다.
avrstudio 컴파일 에러..
mmcu=atmega64 -Wall -gdwarf-2 -std=gnu99 -DF_CPU=8000000UL -Os -funsigned-char -funsigned-bitfields -fpack-struct -fshort-enums -MD -MP -MT main.o -MF dep/main.o.d -c ../main.c
/usr/bin/sh: -Wall: command not found
make: [main.o] Error 127 (ignored)
mmcu=atmega64 -Wl,-Map=TVLHD_2M.map main.o -o TVLHD_2M.elf
/usr/bin/sh: -Wl,-Map=TVLHD_2M.map: command not found
make: [TVLHD_2M.elf] Error 127 (ignored)
avr-objcopy -O ihex -R .eeprom -R .fuse -R .lock -R .signature TVLHD_2M.elf TVLHD_2M.hex
avr-objcopy: 'TVLHD_2M.elf': No such file
make: *** [TVLHD_2M.hex] Error 1
Build failed with 1 errors and 0 warnings...
Help needed.
This seems to be something that the half-brains at Atmel have gone out of their way to ruin in Studio 4.19. Originally Studio had a mechanism where it would look for an find WinAVR if it was installed. Then Atmel started making a half-baked rip-off of WinAVR called "Toolchain" so they modified Studio so it would look for both (and annoyingly it found their crap in preference to WinAVR). It now appears in 4.19 (which is the latest) that they don't even try to look for WinAVR any more. This just shows how shorted sighted Atmel are. When you create a GCC project now you need to go to Project-Configuration Options then on the 5th tab ("Custom options") set the path to avr-gcc to be /winavr/bin/avr-gcc.exe and the path to "make" to be /winavr/utils/bin/make.exe and THEN you should be able to build OK.
시중에 굴러다니는 싸구려 avrusbisp 에 대하여..
사전 정보가 없었기에 어찌 가지고 있다.
다시 한번 명심하라 avrospii 란 걸로 굽는 물건은 사지 말길..
어쨌든 avrospii 가 말을 잘 안 듣는 관계로... winavr 에 포함되어 있는 avrdude라는 프로그래밍툴을 이용해보기로 했다.
문제는 avrusbisp 가 어떤 프로그래머냐..이건데 이것 저것 해본 결과
avr910 이라는 초저가형 프로그래머의 개량판이다.
원래는 시리얼 통신하도록 만든놈인데 ftdi 칩을 사서 usb 라고 버젓히 팔린다는 사실.
오죽하면 avr910 앞에 수식어가 "low cost" 다.
avrdude 를 사용하는 방법을 잘몰라 해매던 중에..
> avrdude -p m8 -b 115200 -c avr910 -P com2 -t
라는 명령을 발견했으니, 대략 매개변수를 설명하자면,
m8 은 atmega8 을 의미한다. 많이 쓰는 atmega128은 유추컨데 m128 로 치환해주면 된다.
-P 뒤가 프로그래머 붙은 com 포트 번호이고 -b 숫자가 보레이트가 되겠다.
-t 로 터미널 모드에서 avrdude를 사용할 수 있다.
아두이노 - 내장 라이브러리 사용 스테핑 모터 구동 소스.

아두이노 - 스테핑 모터 컨트롤러(SLA7062M) 소스
아두이노 wmp 소스
atiny2313 - 테스트 소스.
#include <avr/io.h>
#include <avr/eeprom.h>
#include <avr/interrupt.h>
#include <avr/signal.h>
#define sbi(PORT,BIT) PORT|=_BV(BIT) //set bit
#define cbi(PORT,BIT) PORT&=~_BV(BIT) //clear bit
void delay_us(unsigned int delay) // 1us
{
register unsigned int i;
for(i=0;i<delay;i++)
{
asm volatile("PUSH R0");
asm volatile("POP R0");
asm volatile("PUSH R0");
asm volatile("POP R0");
}
}
void delay_ms(unsigned int time_ms) // 1ms
{
register unsigned int i;
for(i=0;i<time_ms;i++)
{
delay_us(250);
delay_us(250);
delay_us(250);
delay_us(250);
}
}
/********************************************************************************************
string 처리 함수들
*******************************************************************************************/
void __strcpy(char* str1,char* str2)
{
int i = 0;
while(*(str2+i)!= 0) {
*(str1+i) = *(str1+2);
i++;
}
*(str1+i) = '\0';
}
// str : string
// return : size of str
char __strlen(char *str) // verified
{
char ret = 0;
while( (*(str+ret)) != '\0') {
ret++;
if (ret > 100) {
break;
}
}
return ret;
}
void __strcatc(char* str,char c)
{
char j;
j = __strlen(str);
*(str+j) = c;
*(str+j+1) = '\0';
}
void __clrstr(char* str,char size)
{
int i;
for(i = 0; i< size;i++) *(str+i) = '\0';
}
unsigned int __atoi(char* str) // verified
{
char i;
unsigned c;
unsigned int ret =0;
char s = __strlen(str);
for(i=0;i < s;i++) {
c = (*(str + i)) - '0';
ret = ret*10 + c;
}
return ret;
}
void __itoa(char* str,char s,long i) // verified
{
char c;
*(str+s -1) = '\0';
if(i < 0) {
*str = '-';
i = i * -1;
} else {
*str = '+';
}
for(c = s - 2 ;c >= 1;c--) {
*(str+c) = i % 10 + '0';
i = i / 10;
}
}
void __putch(char data)
{
while(!(UCSRA &0X20));
UDR=data;
UCSRA |= 0X20;
}
void send_hex(char data)
{
__putch(data/10 + '0');
__putch(data%10 + '0');
}
void __puts(char* str)
{
do{
__putch(*(str));
str++;
} while(*(str) != '\0');
}
volatile short angle[8] = {0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0};
volatile unsigned char buff[16];
volatile unsigned char buff_offset = 0;
#define DELAY_TIME 2
#define PULSE_WIDTH 50
// 0xffff - 625 = 0xfd82
#define FREQ_TIME 0xfd82
#define MAX_SERVO_VAL 99
SIGNAL(SIG_TIMER1_OVF)
{
asm volatile("cli"); // disable interrupt
int i;
TCNT1=FREQ_TIME;
__putch('s');
PORTB = 0xff;
delay_us(220);
for(i = 0 ;i < 254;i++) {
delay_us(2);
if(i == angle[0]) {
cbi(PORTB,1);
}
if(i == angle[1]) {
cbi(PORTB,2);
}
if(i == angle[2]) {
cbi(PORTB,3);
}
if(i == angle[3]) {
cbi(PORTB,4);
}
}
asm volatile("sei"); // disable interrupt
}
SIGNAL(SIG_USART0_RX )
{
asm volatile("cli"); // disable interrupt
unsigned char c;
c=UDR;
UCSRA |= 0X80;
*(buff + buff_offset) = c;
if(c == 0) {
buff_offset = 0;
angle[0] = buff[0];
angle[1] = buff[1];
angle[2] = buff[2];
angle[3] = buff[3];
angle[4] = buff[4];
angle[5] = buff[5];
angle[6] = buff[6];
angle[7] = buff[7];
}
asm volatile("sei"); // enable interrupt
}
int main()
{
unsigned char c;
// unsigned char buff[30];
unsigned char offset;
asm volatile("cli"); // disable interrupt
DDRB = 0xff; // 1111 1111
DDRD = 0xFE;
// serial set
UCSRA=0X00;
UCSRB=0X98; // (1<<RXEN) | (1<<TXEN); // recieve enalbe, trnas enable..
UCSRC= 0X06; //(1<<USBS) | (3 << UCSZ0); // async, no parity, 1 stop bit
// BAUD = 16M / 16 /(UBRR+1)
// UBRR = 20M / 16 / BAUD - 1
UBRRH=0X00;
UBRRL=0X67; //9600 bps
PORTB = 0x00;
TCCR1B |= 0X05; // pre-scaler : clk/ 1024 = 31250 hz
// 31250 / 625 = 50Hz (20ms)
TCNT1=FREQ_TIME;
// OCR1A=0X001;
TIMSK=(1<<TOIE1); // TOIE1에 인터럽트허용
angle[0] = angle[1] = angle[2] = angle[3] = 120;
asm volatile("sei"); // enable interrupt
c = 'f';
offset = 0;
do {
} while(1);
return 1;
}
max7000시리즈에서 jtag 핀을 IO 핀으로 쓸 수 있을까요? - yes...(2)
Problem
Can I program the four JTAG pins (TCK, TMS, TDI, and TDO) as I/O pins when programming MAX? 7000 devices via a
third-party socket-based programmer?
Solution
Yes. MAX 7000S, MAX 7000A, MAX 7000AE, and MAX 7000B devices allow the user to designate four pins as JTAG pins or user I/O pins. This designation takes place before you compile the design. As a result, the MAX+PLUS? II software generates programming files that specify the pins as either JTAG pins or user I/O pins.If you use a socket-based programmer, you can use a Programmer Object File (.pof), JamTM File (.jam), or Jam Byte-Code File (.jbc) for programming. The Jam File and JBC File support for programming the dual-purpose JTAG pins as I/O pins is only available with socket-based programmers.
하지만 jtag핀을 io핀으로 할당할때 생기는 에러를 막기 위해 컴파일 시에 BST 옵션을 끄면 pof 파일이 제대로 생성이 안된다.
그래서 다시 한번 물어봤다.
답은 이러했다.
Socket based programmer is referring to the programmer such as Altera Programming Unit (APU) at http://www.altera.com/products/devkits/kit-adapters.html When you disable the JTAG BST support, it means that you no longer can program the MAX3000A CPLD using the JTAG ISP from Quartus II programmer, as those JTAG pins of the CPLD are reserved as regular I/O pins already. Although APU is one of the programming unit to program MAX3000A, but it is also not on sale from Altera already. Therefore, you may need the third party tool to program MAX3000A. Kindly please refer to http://www.altera.com/support/devices/programming/max3k/prg-max3k.html for more information.
먼 말인지;;; 된단말이냐 안된단 말이냐.
FPGA 디바이스 CONFIGURATION
1.사이클론 칩은 3가지 형태의 configuration 을 제공한다.
Active Serial, Passive Serial, JTAG-BASE 의 방법이다.
사이클론은 SRAM 베이스로 구현하였기에 전원을 끄면 데이타가 사라진다.
이를 방지하기 위해 CONFIGURATION 롬을 사용하게 되는데
EPC2LO20 같은 칩이 바로 그것이다.
JTAG 만들 이용하여 CONFIGURATION 을 하는 경우에는
전원을 끄면 데이타가 사라지므로,
보통 AS(Active Serial), PS(Passive Serial) 의 방법을 이용하게 된다.
AS 는 EPCS1 이나 EPCS4 시리즈의 칩들을 사용하는 경우에 쓰이며
PS 는 EPC2,EPC4,EPC8,EPC16 등의 칩을 사용하는 경우에 쓰인다.
따라서, 여기서는 PS 만을 언급하겠다.
PS 를 사용하기 위해서는 먼저, 사이클론의 외부 핀중 MSEL0 을 LOW 에 연결하고
MSEL1 에 HIGH 를 연결한다.
2. configuration device 와의 연결
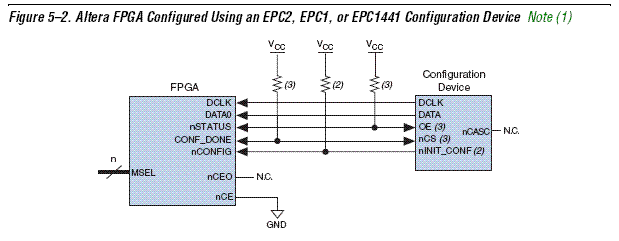
주의할 점은 (3) 이라고 표시된 풀업 저항의 경우에 epc2 의 내부에도 풀업 저항이 있으므로, 만약 (3)을 쓰고
싶으면, 디바이스 내의 풀업 저항을 disable 해줘야 한다.
disable 하는 방법은
쿼터스2 프로그램 -> assignment 메뉴 -> device 선택 -> device and pin button ->
configuration 탭 -> configuration device option 버튼 -> Disalbe nCS and OE pull up... 체크
이 되겠다.
(2)번 저항에 대해서
nINIT_CONF 단자 내에도 칩 내부에 풀업 저항이 있다. 이것은 설정으로 끌 수 없다.
만약 nINIT_CONF 를 사용하지 않는 경우엔 반드시 풀업 저항 혹은 직접 VCC 에 연결해준다.
nCEO는 여러개의 fpga 를 쓸 때 쓰는 핀이다. 하나의 칩만을 쓸때에는 NC(no connection)으로 플로팅 시키며
nCE는 접지 시킨다.
3. JTAG 를 주로 사용할 때에 주의할 점에 대해서, 알테라 사이트 측은 이렇게 써 있다.
Even though other programming or configuration pins (for FPGA) are not used in JTAG mode, they must be properly connected and cannot be left floating.
- nTRST - Driven high during JTAG configuration.
- nCE - Connect to GND or driven low during JTAG configuration.
- MSEL pins - Connect to ground.
- nCONFIG - Driven high or pulled to VCC through a pull-up resistor.
- DCLK - Either pull-up or pull-down through resistor.
- DATA pin(s) - Either pull-up or pull-down through resistor.
- nSTATUS - Pull to VCC through a pull-up resistor. When the device is powered-up, this pin will be released to high.
- CONF_DONE - Pull to VCC through a pull-up resistor. Should be pulled-up individually for the devices in a chain. When the device is successfully configured, this pin will be released to high.
- INIT_DONE - When used, pull-up to VCC.
MAX3000과 MAX7000 시리즈의 차이점.
알테라에 물어봤다.
그들의 대답은 이러하다.
Thank you for selecting our products.
The MAX3000A devices are high performance, low-cost CMOS EEPROM-based programmable logic devices (PLDs) built on a MAX architecture.
The MAX7000 devices are high performance, EEPROM-based programmable logic devices (PLDs) built on second-generation MAX architecture.
The performance of the MAX3000A device is better than the MAX7000 device. The VCCINT power supply of the MAX3000A device is 3.3V.
The VCCINT power supply of the MAX7000 device is 5V. The VCCIO power supply of the MAX3000A device is 3.3V or 2.5V. The VCCIO power supply of the MAX7000 device is 5V or 3.3V.
These are the main differences. Hope it is helpful to you. If you have any queries, please don’t hesitate to contact me. Have a good afternoon.
요지를 보자면
max7000은 max시리즈의 second generation 이라고 한다. max3000 의 성능이 좋으며, 전압도 3.3V 구동한다.
나머지는 차이가 없는듯.





